|
Reference DNA was extracted from peripheral blood cells of healthy
people.
cCGH:
Tumor DNA and reference DNA were labeled by
nick translation. The
hybridization mixture contained of 400 ng tumor DNA
and
reference DNA, and 10
µg
unlabeled human Cot-1 DNA (Gibco/BRL, Life Technologies, Gaithersburg,
MD) dissolved in 10
mL
hybridization buffer. The denatured hybridization mixture was hybridized
to the slide with normal metaphase spreads.
aCGH: Labeling the
6 µg
of tumor and reference DNA Cy3-dUTP and Cy5-dUTP.
CGH was executed on individual and pooled DNA from the LMS samples,
divided according to both grade and the presence of DNA copy number
changes in 17p.
At last, analyzed the hybridized slides using an Olympus fluorescence
microscope and the ISIS digital image analysis system (
MetaSystems GmbH, Altlussheim, Germany
).Agilent G2565AA Feature Extraction Software.
Array CGH was performed on the
Agilent cDNA microarray consisted of 13,000 cDNA clones, and using
the DNA pooled for cCGH. And the pooled method could detect the
biological meaning.
Sample pooling reduced the effects of biological variation on gene
expression arrays and comparable expression measurements from pools and
individuals
The array CGH smooth software determines breakpoints within chromosomes
by performing maximum likelihood estimation.
Obtains of DNA sequence copy number were most commonly observed in
chromosomes 1 (43%), 5 (29%), 8 (29%), 17 (43%), and 20 (29%).
Losses most frequently influenced chromosomes 2 (43%), 6 (50%), 10
(57%), 13 (71%), 16 (43%), and X (50%)
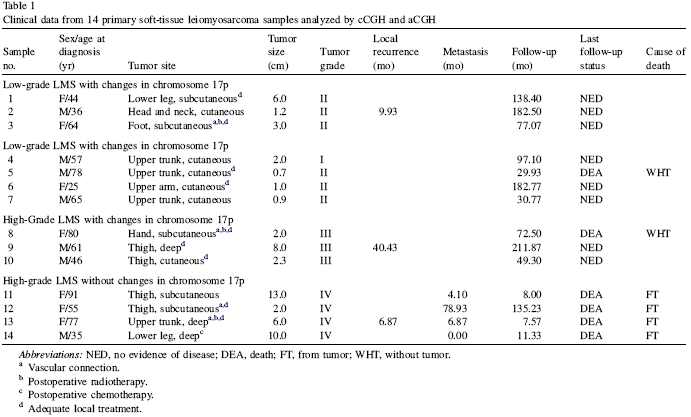
From the Table 1, we could find out the
clinical characteristics are shown above. The samples 1-7 are low-grade
(
I
&
II
), 8-14 are high-grade(
III
&
IV
). The
IV
Importantly, pooled aCGH displayed all the changes that were frequent in
the nonpooled approach. Hence, the array results from the pooled
approach can be interpreted as characteristic biologically significant
changes in LMS, even when some less frequent changes may have remained
undetectable in our pool.
The pooled approach showed amplified genes only in the 17p amplicon pool
but not in the pool without changes in 17p.
All of 14 LMS samples showed changes with a mean value of 9.71
±
1.61 aberrations per sample (range, 2–20). Gains of DNA copy number
changes were less frequent than losses (gains/losses
5
1.0:1.3), with mean values of 3.86
±
0.57 (range, 0–7) and 5.00
±
1.17 (range, 0–13) changes per sample, respectively.
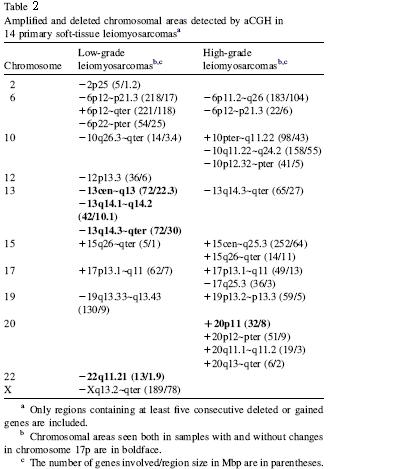
Other fewer frequent gains, high-level amplifications, and losses are
described
in
Fig. 1 and
Fig.
2,
for
low- and high-grade
LMS samples, respectively.
cCGH:
Despite of the tumor grade, the minimal common regions of gain in DNA
pooled from all 14 LMS samples were narrowed down to
1cen~q21 (cases
8–10 in the high-grade LMS pool with aberrations in chromosome 17p, and
cases 1–3 in the low-grade LMS pool with aberrations in chromosome 17p)
as well as 19p (cases 1–3 in the low-grade LMS pool with changes in
chromosome 17p).
aCGH:
Despite of the tumor grade, the minimal common regions of gene
amplifications in the DNA pools were narrowed down to 15q26~qter (50.0%;
cases 1–3 in the low-grade LMS pool with aberrations in 17p, and cases
8–10 in the high-grade LMS pool with changes in 17p) as well as
17p13.1~q11 (50.0%; cases 1–3 in the low-grade LMS pool with aberrations
in 17p, and cases 8–10 in the high-grade LMS pool with changes in 17p).
The aCGH results
Table
2
showed that the number of areas affected by gene copy number losses
in the low-grade LMS pool
(10 areas) was higher in comparison to the high-grade LMS pool (7
areas). And gains in high-grade tumors (9 areas) were threefold
in comparison to low-grade tumors (3 areas). This advice an increasing
trend in the number of gene DNA sequences during the progression of LMS.
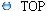
Array CGH results revealed 25 changed chromosomal regions (at least five
consecutive genes gained or lost) involving a total of 2218 genes.
Previous cCGH reports demonstrate that among the most significant DNA
copy number changes in LMS are losses in 10q and 13q, as well as gains
in 16p and gains and/or amplifications in 17p.
The cCGH results did not reveal any novel amplicons or losses, but all
previously mentioned changes were found in all samples,
despite
of the tumor grade. Therefore we suggest that these changes may harbor
genes involved in the tumor genesis of LMS.
E.g.
17p13.1~q11
means:
17:
chromosome
17
q:
means
chromosome
q arm (longer arm)
below the centromere.
21:
means two-one (part two-length one), not twenty-one.
Recombination
rate
Means the size of 1 recombination rate.
|


